What is the Customer Effort Score (CES)?

In addition to the Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) and the Net Promotor Score (NPS), the Customer Effort Score is another important key figure for measuring and interpreting customer satisfaction.
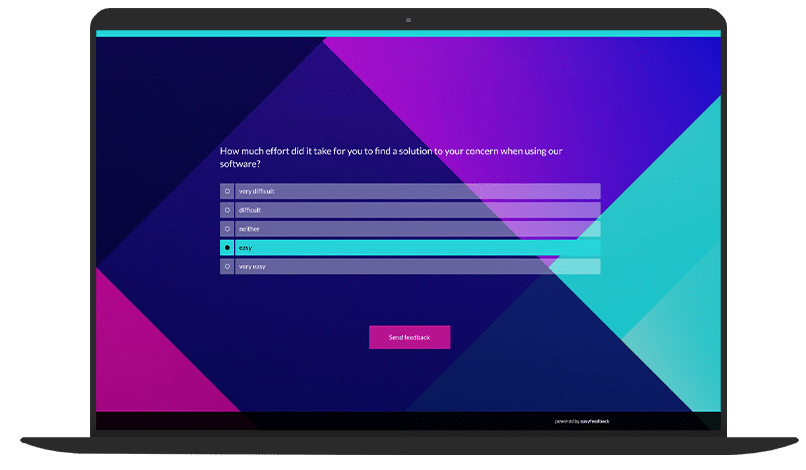
Using a scale of 1 (extremely easy) to 7 (extremely difficult), it provides information on how uncomplicated an interaction with your company/product was from your customers’ point of view, in order to implement measures to optimize and reduce the complexity of interactions and enhance the user experience based on this.
For example, customer satisfaction is measured and interpreted via the question: “How easy was it to find the right contact person for your request?”.
Additionally, the Customer Effort Score provides insight into customer satisfaction, which contributes to customer loyalty.
In the rapidly growing competitive field of any industry, it is important to measure customer loyalty in order to minimize churn rates.
What is the difference between the CES, the NPS and the CSAT?
Although it is possible to measure and interpret customer satisfaction with all three metrics mentioned, they nevertheless differed in terms of the focus of the survey.
While the Customer Effort Score asks about customer satisfaction via the effort customers put into solving their problem or interacting with the company/product, the Net Promotor Score measures customer satisfaction via the willingness to recommend the company/product to others via a scale from 0 (unlikely) to 10 (very likely).
The Customer Satisfaction Score, on the other hand, measures customer satisfaction based on a specific interaction, such as the ordering process or the information content of the website. The CSAT survey participant can provide feedback on a scale between 1 (very dissatisfied) to 5 (very satisfied).
As you can see, while all three metrics measure your customers’ satisfaction, they focus on different areas of emphasis in the survey: Effort measurement, willingness to recommend, and satisfaction measurement related to a specific process.

So, depending on your use case, you can choose the appropriate metric to measure customer satisfaction or collect all metrics to get a more comprehensive picture of your customers’ satisfaction.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the Customer Effort Score?
Every method and every metric has its advantages and disadvantages. So does the Customer Effort Score.
As you already know, the CES gives you a good overview of how much effort a customer has to put in to solve a problem or concern with a product, for example, or to make a purchase.
The short survey thus uncovers potential and helps you to specifically address the areas that require optimization in order to reduce the customer’s effort as much as possible and thus increase customer satisfaction.
But the CES survey can also be helpful in areas that have already been optimized. For example, you can find out whether the adjustments you have made are having the desired effect or whether you need to make further adjustments.
The CES survey itself is easy to create. It is based on just one question. As a result, the survey is short and the time required to answer it is low. This has a positive effect on the participation rate, which is relatively high for the CES.
The evaluation of the survey also requires little time if it contains one question.
The disadvantage of this metric is that – like the Customer Satisfaction Score – it only reflects a snapshot of the participant. In addition, the perception of effort is always subjective, as participants have different views on how to measure effort for themselves.
In addition, the CES has no predictive power about how the customer will behave in the future. That means whether he will become a repeat buyer, whether he will recommend your company positively or whether he will look for alternative ones.
So that you can read all the advantages and disadvantages of the Customer Effort Score again, I have summarized them briefly here:
Advantages:
- Short & easy to understand survey
- High participation rate due to low response effort
- Evaluation also possible with little time expenditure
- Reveals potentials to carry out optimizations
Disadvantages:
- Only a subjective snapshot
- Participants have different perceptions of the effort required
- No informative value about the future behavior of the customer
How to apply the Customer Effort Score?
There are many ways to determine customer satisfaction using the Customer Effort Score.
For example, you can apply the CES survey after each email or phone contact with your support to ask how smooth the interaction was with the support or agent.
Furthermore, you can measure your customers’ effort after each of your help articles. This will help you find out how quickly your customers were able to find the answer to their questions.
Another possible use case would be to survey how much effort customers had to put in to solve a problem with your product.
As you can see, the CES survey can be used flexibly for many scenarios. But especially when it comes to asking about the customer experience in terms of the effort required to fix a problem.
Are there any tips on how to use the Customer Effort Score?

Yes, there are. Below we have compiled tips for the application of the Customer Effort Score:
Tip 1: Ask immediately after the interaction.
The sooner you ask your customer about the complexity of the interaction, the fresher their memory and the more valuable the feedback. Therefore, don’t wait too long to survey, not only can the quality of the feedback suffer, but so can the willingness to participate in the effort survey.
Tip 2: Use regularly
In order for CES to help you determine customer satisfaction and effort after each interaction with your company or product, you need to use the CES survey regularly and over time.
Only then will you be able to tell if your customers had a positive or negative experience with the interaction options you provided, such as contacting your support or reading your help articles.
Tip 3: Don’t use a welcome page.
Start the CES survey directly with the interaction effort question.
A welcome page with text and information can already lead to abandonment, as the participant thinks it is a longer survey. However, in the end, the participant only has to answer a single question.
Tip 4: Respond to feedback
If you have enough feedback on one of your offered interactions, then depending on whether the feedback is negative or positive, you should respond to it. Nothing is worse than letting the feedback go unused and not striving for improvement.
How is the Customer Effort Score calculated?
Calculating the CES is relatively simple and can be done in two ways.
Basically, the participants of the CES survey indicate the effort of an interaction with your product or company using a scale from 1 (extremely easy) to 7 (extremely difficult).
Now, to calculate your Customer Effort Score, you can either use the average of all scores:
CES = Summer of Scores / Number of Scores
or
you can do the calculation in the style of the Net Promotor Score.
This means that the participants’ answers are divided into three categories. The first category includes the participants who rated the interaction with a score of 1 or 2. These are the customers who had a low effort with the interaction.
The second category is formed by the participants who gave the grade 3 or 4. These are the customers who had a medium effort. In the last category come all the participants who gave the score 5 to 7 in the CES survey and thus had a high effort with the interaction.
Now the Customer Effort Score is calculated according to the Net Promotor Score method as follows:
CES = Percentage of participants with a high effort score (%) - Percentage of participants with a low effort score (%).
The resulting value ranges from -100% to +100%. Where -100 % is the worst value and +100 % is the best value.
What is a good CES score?
Unfortunately, it is not possible to say exactly.
However, the closer the CES score is to +100% according to the NPS calculation or to 1 when calculated according to average scores, the less effort customers had to put into the interaction or solving their problem.
If, for example, an interaction results in a CES score of less than 0 (in the NPS calculation) or >6 (as an average score), then this is an indication that the interaction involves a lot of effort for the customer.
Thus, there is a need for action for your company to improve the user experience and satisfaction.
Conclusion: Gain insight into customer loyalty with the CES
If you want to increase customer experience and satisfaction, you need metrics you can rely on to take action to improve or test for success.
CES, along with NPS and CSAT, is another possible metric you can use to inquire about and interpret customer satisfaction via the customer’s perception of effort to resolve their issue or to measure the degree to which an interaction with your company/product was uncomplicated.
That the CES, like other metrics, has drawbacks is not objectionable.
But as an additional indicator in combination with other metrics, it can give you a comprehensive picture of your customer’s satisfaction.
So you, too, figure out the complexity of your customers’ interactions and problem solving to optimize their satisfaction and experience with your company and products.
Use the possibility of regular and simple CES surveys and that best with easyfeedback ;).
More about Customer Experience
- Everything you need to know about Customer Experience (CX)!
- Creating positive customer experiences with customer experience management
- 3 touchpoints in the customer experience (with video)
- Your way to an effective customer experience strategy!
- 10 methods to analyze the customer experience
- 12 practical examples for improving the customer experience
- 10 metrics to measure Customer Experience
- Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) – Measuring Customer Satisfaction differently
- Everything you need to know about the Net Promoter Score (NPS)!
- Churn Rate: Key metric for measuring customer loyalty
- The Customer Satisfaction Index (CSI): A key to measuring customer satisfaction




