What does customer relationship mean?
Customer relationship describes the entirety of all interactions and bonds between a company and its customers—from the initial contact to long-term loyalty.
It’s about more than just transactions.
It’s about trust, communication, added value, and emotional connection.
Customer relationships can be divided into three phases:
- Initiation: Initial points of contact such as advertising, social media, or a visit to the website.
- Development: The first purchases, consultations, and interactions that determine whether a prospect becomes a loyal customer.
- Retention: Maintaining the relationship through service, communication, offers, and feedback mechanisms.
Why are strong customer relationships so important?
1. Competitive advantage
In saturated markets, price and quality are no longer the only differentiating factors.
Customer loyalty and emotional attachment offer a strategic advantage.

2. Higher customer lifetime value (CLV)
Satisfied, loyal customers buy more often, spend more money, and remain loyal for longer—which increases sales in the long term.
3. Word of mouth and recommendations
Recommendations from enthusiastic customers are often more credible and effective than traditional advertising.
4. Source of feedback
Customers who feel valued share their opinions – this provides valuable information for the further development of products and services.
Customer care tools and strategies
1st tool: CRM systems (customer relationship management)
Modern software solutions help to collect and evaluate customer data and take targeted measures.
A good CRM system provides a 360-degree view of the customer.
2nd tool: Personalization
Customers expect tailored communication.
From personalized newsletters to individual offers—those who feel understood will stay.

3rd tool: Customer service and support
Quick responses, expert advice, and solution-oriented support are key factors for trust and satisfaction.
4th tool: Customer loyalty programs
Discounts, loyalty points, or exclusive benefits motivate customers to return and strengthen the relationship.
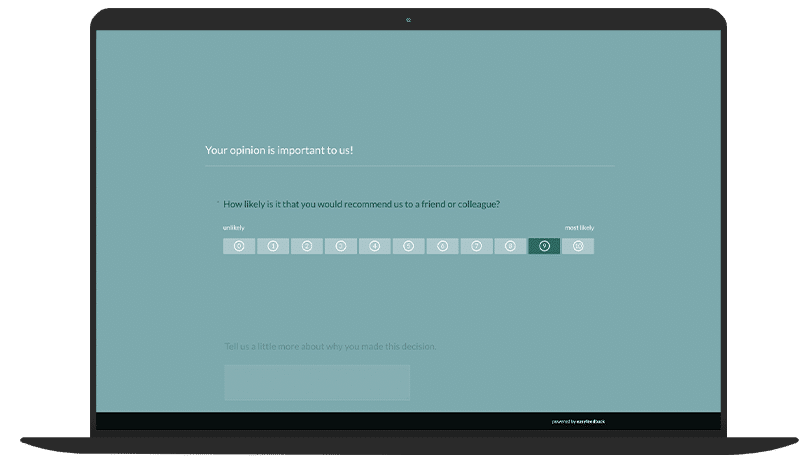
5th tool: Surveys
Regular customer surveys provide valuable insights into needs, satisfaction, and potential for improvement.
They also signal that “your opinion matters.” Targeted surveys—e.g., after a purchase or as part of an NPS (Net Promoter Score)—allow you to better understand customer wishes and derive targeted measures.
6th tool: Emotional intelligence
Genuine relationships are built on empathy, attentiveness, and authenticity.
Companies that operate with “heart” create genuine brand loyalty.
Challenges in customer relationship management
- Digitalization makes personal contact more difficult, but at the same time opens up new avenues for intelligent customer communication.
- Data protection is a sensitive issue—transparency and trust are crucial here.
- Customer expectations are constantly rising. Companies must act quickly, flexibly, and in a service-oriented manner.
The future of customer relations: humans + machines
The future lies in the synergy between technology and humanity.
Artificial intelligence analyzes data, predicts needs, and automates processes—but the decisive difference still lies in interpersonal contact.
Chatbots, personalized algorithms, and voice assistants are only effective if they convey a feeling of genuine closeness.
Conclusion: Relationships instead of indifference
In a rapidly changing world, one thing remains constant: the desire for connection.
Customer relationships are not a one-way street, but a dialogue.
Companies that listen, understand, and act individually create trust—and trust is the hardest currency of the future.
It is not always the big advertising campaigns that retain customers, but the small, honest gestures.
The art lies not only in selling, but in connecting.



