What is leadership competence?
Leadership competence describes the ability to motivate, inspire and lead people in a targeted manner.

It encompasses professional as well as social and emotional skills, including
- Strong communication skills
- Empathy
- Decision-making skills
- Conflict resolution skills
- Strategic thinking
- Sense of responsibility
Why is it important to measure leadership skills?
The systematic measurement of leadership competence is a central component of modern personnel and organizational development.
It makes it possible to identify leadership potential at an early stage and promote it in a targeted manner.
On this basis, tailor-made development measures can be derived that strengthen individual strengths and specifically address existing areas for development.
At the same time, a well-founded assessment of leadership skills helps to avoid misappointments to management positions – a challenge that can have not only economic but also cultural consequences for organizations.
In addition, the systematic recording of leadership behavior supports the establishment and further development of a consistent, value-based leadership culture that contributes to the long-term success of the company.
Methods for measuring leadership competence
1. Method: 360-degree feedback
In 360-degree feedback, the manager is assessed from different perspectives – by superiors, colleagues, employees and, if necessary, external partners.
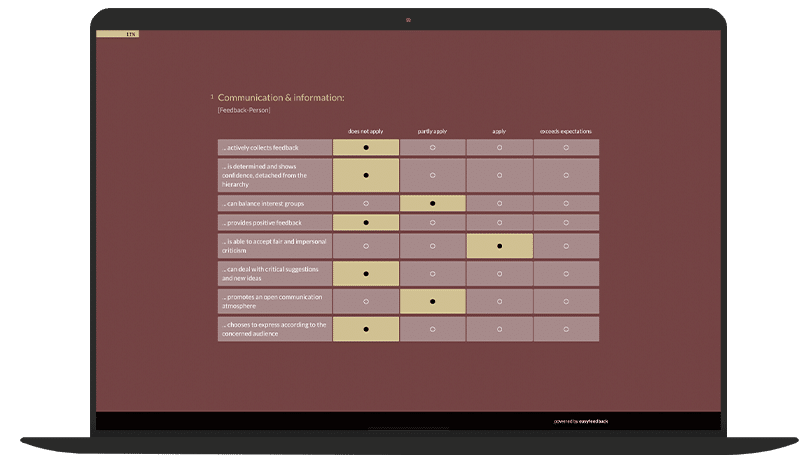
This method provides a comprehensive picture and identifies both self-perception and the perception of others.
Advantages: Diverse perspectives, high informative value
Disadvantages: Subjectivity, high effort
2nd method: Behavior-based interviews and assessment centers
Managers are confronted with concrete, practical situations in order to observe and evaluate their leadership behavior.
Examples:
- Case studies
- Role plays
- Group discussions
Advantages: Realistic, direct observation
Disadvantages: Costly and time-consuming
3rd method: Self-assessment and psychometric tests
Questionnaires such as the Leadership Effectiveness Analysis (LEA) or the MBTI profile help to analyze personality traits and leadership styles.
Advantages: Fast and scalable
Disadvantages: Risk of distortion due to self-image
4th method: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Hard key figures can also allow conclusions to be drawn about leadership competence, e.g:
- Employee turnover
- Team performance
- Sickness rates
- Achievement of strategic goals

Advantages: Objectivity, comparability
Disadvantages: Context dependency, no cause clarification
Challenges in measuring
Despite numerous established methods, measuring leadership competence remains a challenging task.
A major problem lies in the subjectivity of many methods: Whether in feedback processes, interviews or self-assessments – personal perceptions and individual judgments influence the evaluation and can lead to distortions.
Added to this is the context dependency of leadership: a manager who is successful in a certain team or company does not necessarily have to be equally effective in a different environment.
Leadership is always embedded in specific framework conditions, corporate cultures and expectations.
Moreover, leadership is not a static concept.
Competencies continue to develop – with growing experience, through new challenges or in the course of organizational changes.
This means that a snapshot is not enough.
Leadership skills must be assessed regularly and continuously reflected upon in order to do justice to their dynamic nature.
Conclusion
Measuring leadership competence is complex – but possible.
The combination of different methods is crucial in order to obtain a realistic and holistic picture.
It is not only the measurement itself that is important, but above all the derivation of specific development measures.
Because good leadership can not only be recognized – it can also be promoted.




